Notes On Springboot
References
- Swagger: API first approach
- Spring Framework definition
- DispatcherServelet
- Spring vs SpringBoot
- Data Access Object
Spring Framework
- A framework that lets you write Java Enterprise applications.
- At the heart are the modules of the core container, including a configuration model and a dependency injection mechanism.
- Provides foundational support for different application architectures, including messaging, transactional data and persistence, and web.
- It also includes the Servlet-based
Spring MVCweb framework and, in parallel, theSpring WebFluxreactive web framework.
Spring Framework’s Inversion of Control (IoC) container
- IoC is also known as dependency injection (DI).
- It is a process whereby objects define their dependencies (that is, the other objects they work with) only through constructor arguments, arguments to a factory method, or properties that are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method.
- The container then injects those dependencies when it creates the bean.
- The following example shows the basic structure of XML-based configuration metadata. This configuration metadata represents how you, as an application developer, tell the Spring container to instantiate, configure, and assemble the objects in your application.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- dependencies and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- dependencies and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>Beans
- In Spring, a bean is an object that the Spring container instantiates, assembles, and manages.
- A Spring IoC container manages one or more beans.These beans are created with the configuration metadata that you supply to the container (for example, in the form of XML
<bean/>definitions). - Within the container itself, these bean definitions are represented as
BeanDefinitionobjects. - A bean definition is essentially a recipe for creating one or more objects.
- The container looks at the recipe for a named bean when asked and uses the configuration metadata encapsulated by that bean definition to create (or acquire) an actual object.
- Spring framework gives access to a lot of modules that make writing production level code easier.
- For example, in the early days of Java web development, we needed to write a lot of boilerplate code to insert a record into a data source. By using the
JDBCTemplateof theSpring JDBCmodule, we can reduce it to a few lines of code with only a few configurations. - Spring requires defining the dispatcher servlet, mappings, and other supporting configurations. We can do this using either the
Deployment Descriptorfileweb.xmlor anInitializerclass.
Example Spring Application using WebApplicationInitializer
- Java configuration typically uses
@Bean-annotatedmethods within a@Configurationclass. The@Beanannotation on a method indicates that the method creates a Spring bean. Moreover, a class annotated with@Configurationindicates that it contains Spring bean configurations.
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context
= new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("com.baeldung");
container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(context));
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = container
.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(context));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}- We also need to add the
@EnableWebMvcannotation to a@Configurationclass, and define a view-resolver to resolve the views returned from the controllers:
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
public class ClientWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver bean
= new InternalResourceViewResolver();
bean.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
bean.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/view/");
bean.setSuffix(".jsp");
return bean;
}
}Example Spring Application using web.xml
- Controller:
HelloController.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)public String printHello(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello Spring MVC Framework!");
return "hello";
}
}web.xml: Notice we are mappingHelloWorldservelet with/url pattern. A web container can have multiple such servelets for for different url patterns, all defined statically in the deployment descriptorweb.xmlfile
<web-app id = "WebApp_ID" version = "2.4"
xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Spring MVC Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloWeb</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloWeb</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>- Finally, the Spring configuration of the servelet in the
HelloWeb-servlet.xml:
<beans xmlns = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package = "com.tutorialspoint" />
<bean class = "org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name = "prefix" value = "/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<property name = "suffix" value = ".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>- and the following is the Spring view
.jspfile
<%@ page contentType = "text/html; charset = UTF-8" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>${message}</h2>
</body>
</html>- Spring bootstrapping
Servletcontainer (the server) readsweb.xml.- The
DispatcherServletdefined in theweb.xmlis instantiated by the container. DispatcherServletcreatesWebApplicationContextby readingWEB-INF/{servletName}-servlet.xml.- Finally, the
DispatcherServletregisters the beans defined in the application context. com.tutorialspointpackage is scanned, a controller class is found that can respond to web requests.
Spring Boot
- Makes it easy to create (bootstrap) standalone production grade Spring application.
- Chooses convention over configuration to bootstrap an application that just runs.
- Spring Boot offers a fast way to build applications. It looks at your classpath and at the beans you have configured, makes reasonable assumptions about what you are missing, and adds those items. With Spring Boot, you can focus more on business features and less on infrastructure.
- Is Spring MVC on the classpath? There are several specific beans you almost always need, and Spring Boot adds them automatically. A Spring MVC application also needs a servlet container, so Spring Boot automatically configures embedded Tomcat.
- Is Jetty on the classpath? If so, you probably do NOT want Tomcat but instead want embedded Jetty. Spring Boot handles that for you.
- Is Thymeleaf on the classpath? If so, there are a few beans that must always be added to your application context. Spring Boot adds them for you.
- Spring applications generally create a WAR file that then needs to be deployed to a servlet (eg tomcat) container. Springboot instead creates a standalone application with embedded webserver in it (no need for a separate servlet container).
- Spring Boot does not generate code or make edits to your files. Instead, when you start your application, Spring Boot dynamically wires up beans and settings and applies them to your application context.
- The entry point of a Spring Boot application is the class which is annotated with @SpringBootApplication:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}- It also takes care of the binding of the
Servlet,Filter, andServletContextInitializerbeans from the application context to the embedded servlet container.
Spring Web MVC
- MVC is known as an architectural pattern, which embodies three parts Model, View and Controller, or to be more exact it divides the application into three logical parts: the model part, the view and the controller.
- It was used for desktop graphical user interfaces but nowadays is used in designing mobile apps and web apps.
- The model is responsible for managing the data of the application. It receives user input from the controller.
- The view renders presentation of the model in a particular format.
- The controller responds to the user input and performs interactions on the data model objects. The controller receives the input, optionally validates it and then passes the input to the model.
- The Spring Web model-view-controller (MVC) framework is designed around a DispatcherServlet that dispatches requests to handlers, with configurable handler mappings, view resolution, locale and theme resolution as well as support for uploading files.
- The default handler is based on the
@Controllerand@RequestMappingannotations, offering a wide range of flexible handling methods. - Spring’s web MVC framework is, like many other web MVC frameworks, request-driven, designed around a central servlet that dispatches requests to controllers and offers other functionality that facilitates the development of web applications.
- Spring’s
DispatcherServlethowever, does more than just that. It is completely integrated with the Spring IoC container and as such allows you to use every other feature that Spring has. - The
DispatcherServletis an expression of the “Front Controller” design pattern. A front controller is defined as a controller that handles all requests for a Web Application.DispatcherServletservlet is the front controller in Spring MVC that intercepts every request and then dispatches requests to an appropriate controller.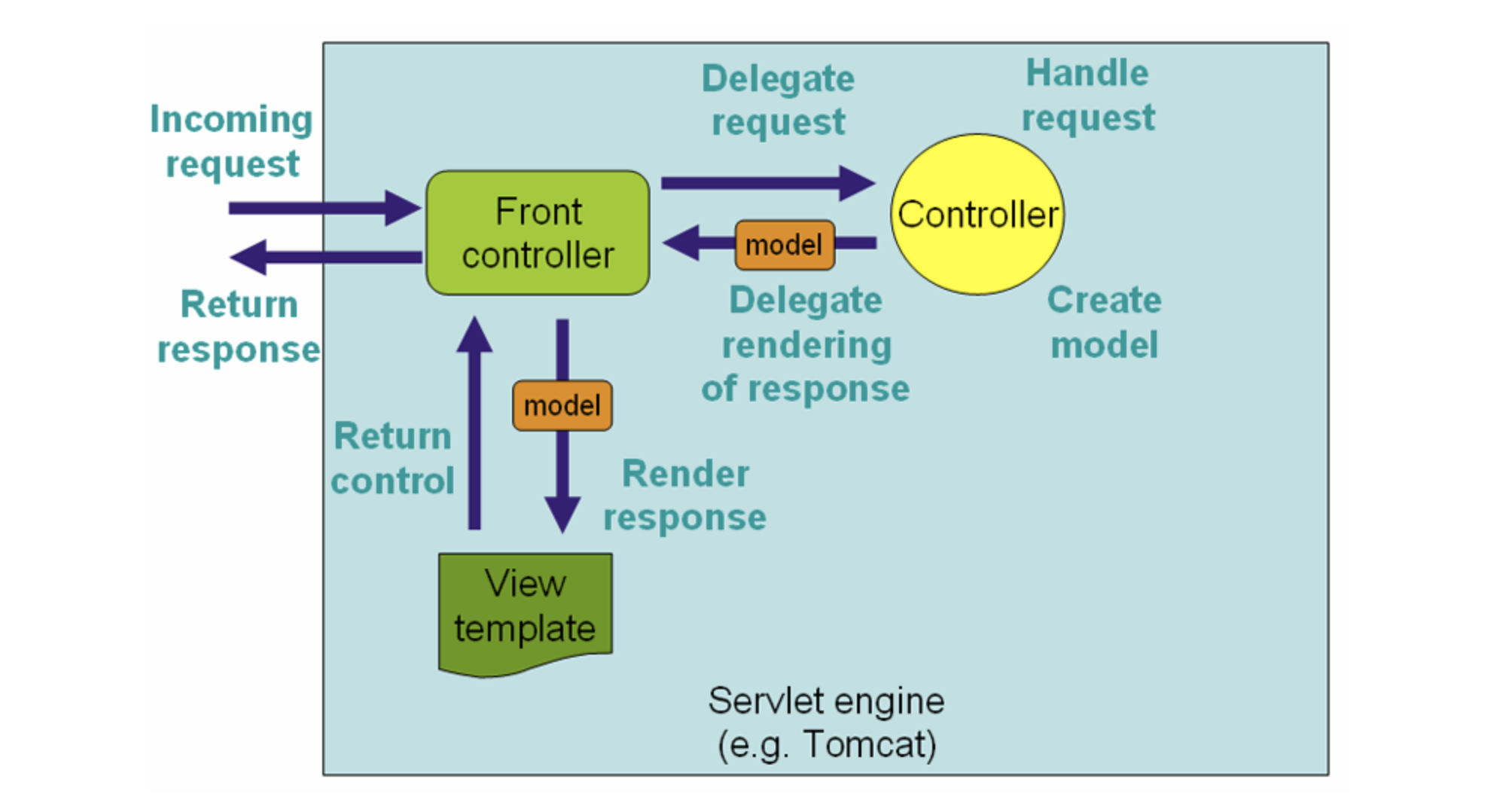
Data Access Object Pattern in JAVA
- DAO pattern is a structural pattern that allows us to isolate the application/business layer from the persistence layer (usually a relational database, but it could be any other persistence mechanism) using an abstract API.
- The functionality of this API is to hide from the application all the complexities involved in performing CRUD operations in the underlying storage mechanism.
EntityManageris an interface used to interact with the persistence context.- Domain class, that defines our domain model.
public class User {
private String name;
private String email;
// constructors / standard setters / getters
}- DAO API, an interface that defones abstract API that performs CRUD operattions on Object T.
public interface Dao<T> {
Optional<T> get(long id);
List<T> getAll();
void save(T t);
void update(T t, String[] params);
void delete(T t);
}- Defining a
User-specific implementation ofDaoclass.
public class UserDao implements Dao<User> {
private List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
public UserDao() {
users.add(new User("John", "john@domain.com"));
users.add(new User("Susan", "susan@domain.com"));
}
@Override
public void save(User user) {
users.add(user);
}
@Override
public void update(User user, String[] params) {
user.setName(Objects.requireNonNull(
params[0], "Name cannot be null"));
user.setEmail(Objects.requireNonNull(
params[1], "Email cannot be null"));
users.add(user);
}
@Override
public void delete(User user) {
users.remove(user);
}
}- For simplicity’s sake, the
usersList acts like an in-memory database, which is populated with a couple of User objects in the constructor. - An application using the
UserandUserDaoclass. Observer, howUserDaohides from the application all the low-level details on how the objects are persisted, updated, and deleted.
public class UserApplication {
private static Dao<User> userDao;
public static void main(String[] args) {
userDao = new UserDao();
User user1 = getUser(0);
System.out.println(user1);
userDao.update(user1, new String[]{"Jake", "jake@domain.com"});
User user2 = getUser(1);
userDao.delete(user2);
userDao.save(new User("Julie", "julie@domain.com"));
}
private static User getUser(long id) {
Optional<User> user = userDao.get(id);
return user.orElseGet(
() -> new User("non-existing user", "no-email"));
}
}- DAO can be used as an abstraction over JPA’s entity manager. Sometimes we just want to expose to our application only a few domain-specific methods of the entity manager’s API.
public class JpaUserDao implements Dao<User> {
private EntityManager entityManager;
// standard constructors
@Override
public Optional<User> get(long id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(entityManager.find(User.class, id));
}
@Override
public List<User> getAll() {
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("SELECT e FROM User e");
return query.getResultList();
}
@Override
public void save(User user) {
executeInsideTransaction(entityManager -> entityManager.persist(user));
}
@Override
public void update(User user, String[] params) {
user.setName(Objects.requireNonNull(params[0], "Name cannot be null"));
user.setEmail(Objects.requireNonNull(params[1], "Email cannot be null"));
executeInsideTransaction(entityManager -> entityManager.merge(user));
}
@Override
public void delete(User user) {
executeInsideTransaction(entityManager -> entityManager.remove(user));
}
private void executeInsideTransaction(Consumer<EntityManager> action) {
EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();
try {
tx.begin();
action.accept(entityManager);
tx.commit();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
tx.rollback();
throw e;
}
}
}- The use of Composition and Dependency Injection allows us to call only the entity manager methods required by our application.
- The
UserApplicationclass can have aJpaUserDaomember object injected into it, and be completely unaware of how the persistence layer performs CRUD operations.
Spring Data
- Spring Data makes it possible to remove the DAO implementations entirely. The interface of the DAO is now the only artifact that we need to explicitly define.
- In order to start leveraging the Spring Data programming model with JPA, a DAO interface needs to extend the JPA specific Repository interface,
JpaRepository. This will enable Spring Data to find this interface and automatically create an implementation for it.
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> {
}- When Spring Data creates a new Repository implementation, it analyses all the methods defined by the interfaces and tries to automatically generate queries from the method names. Eg,
save,findOne,findAll(Sort),findAll(Example). - custom query can also be defined via the @Query annotation:
@Query("SELECT f FROM Foo f WHERE LOWER(f.name) = LOWER(:name)")
Foo retrieveByName(@Param("name") String name);- The actual implementation of the Spring-managed DAO is indeed hidden since we don’t work with it directly. It’s a simple enough implementation, the
SimpleJpaRepository, which defines transaction semantics using annotations. SimpleJpaRepository: Default implementation of theorg.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepositoryinterface. This will offer you a more sophisticated interface than the plainEntityManager.- This uses a read-only
@Transactionalannotation at the class level, which is then overridden for the non-read-only methods. The rest of the transaction semantics are default, but these can be easily overridden manually per method. - Spring Data JPA doesn’t depend on the old ORM templates (JpaTemplate, HibernateTemplate)
- Exception translation, that were provided by DAOs, is still enabled by the use of the
@Repositoryannotation on the DAO. This annotation enables a Spring bean postprocessor to advise all @Repository beans with all the PersistenceExceptionTranslator instances found in the container, and provide exception translation just as before. - We can also use the Spring Boot Starter Data JPA dependency that will automatically configure the DataSource for us. We need to make sure that the database we want to use is present in the classpath. The explicit configuration for a standard Spring application is now included as part of Spring Boot auto-configuration.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:1234/sampleappdocker
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=trueBeans
- Beans are used when you need a long lived instance (mostly the lifetime of the service) of an object.
- Beans are singleton. Beans have a single instance of an object running, and keep getting reused.
- Dependent classes use Dependency Injection to access the instance of the bean. (eg using
@Autowired). - Beans can be created using many annotations. eg
@Bean,@Component,@Service,@Controlleretc.
class Foo {
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
class Bar {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public void test() {
// Doesn't have to initialize or construct a RestTemplate object.
restTemplate.exchange(...);
}
}@Component(and@Serviceand@Repository) are used to auto-detect and auto-configure beans using classpath scanning. There’s an implicit one-to-one mapping between the annotated class and the bean (i.e. one bean per class). Control of wiring is quite limited with this approach, since it’s purely declarative.@Beanis used to explicitly declare a single bean, rather than letting Spring do it automatically as above. It decouples the declaration of the bean from the class definition, and lets you create and configure beans exactly how you choose.- Let’s imagine that you want to wire components from 3rd-party libraries (you don’t have the source code so you can’t annotate its classes with
@Component), so automatic configuration is not possible. The@Beanannotation returns an object that spring should register as bean in application context. The body of the method bears the logic responsible for creating the instance. - The
@Repositoryannotation is a marker for any class that fulfils the role or stereotype of a repository (also known as Data Access Object or DAO) - The
@Controllerannotation indicates that a particular class serves the role of a controller. The dispatcher scans the classes annotated with @Controller and detects methods annotated with@RequestMappingannotations within them. We can use@RequestMappingon/in only those methods whose classes are annotated with @Controller and it will NOT work with@Component, ``@Service,@Repository`. @Servicebeans hold the business logic and call methods in the repository layer. Apart from the fact that it’s used to indicate, that it’s holding the business logic, there’s nothing else noticeable in this annotation.
Swagger-SDK
- API as first class objects:
- codegen can be used to create yaml to model, and the
swagger-sdkmodel classes are used as dependency in server project. - the codegen is generated from
server/**/resources/public/*.yaml, ie the public APIs defined for the service. (egDoSomethingRequest: yaml object that defines the request body fordoSomething) - swagger-sdk can also has
src/java/**/*.javafiles to add more supporting classes, generally used for exposing internal classes that are not needed in API documentation, but maybe needed for using the SDK (for example, model files). - Both yaml (public class) and internal java files (internal class) are avaible in SDK. The SDK is used by
./serverand./server. api-doc-external.yamlis the external API endpoint. It is used to create the documentation for REST APIs and also generates “client” classes and function to use these API through an SDK.
/orgs/{orgId}/deployments/{deploymentId}/object/{objectId}/operations/doSomething:
post:
tags:
- Foo Bar Service
summary: Do Something
description: Do this something for specified object
operationId: doSomething
parameters:
- $ref: '#/parameters/orgIdPathParam'
- $ref: '#/parameters/sddcIdPathParam'
- $ref: '#/parameters/objectIdPathParam'
responses:
'200':
description: OK
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/Operation'- gets converted into something like:
public class FooBarServiceApi
public Operation doSomething(UUID orgId, UUID sddcId, UUID objectId) throws RestClientException {
uriVariables.put("orgId", orgId);
uriVariables.put("sddcId", sddcId);
uriVariables.put("objectId", objectId);
String path = UriComponentsBuilder.fromPath(
"/orgs/{orgId}/deployments/{deploymentId}/object/{objectId}/operations/doSomething")
.buildAndExpand(uriVariables)
.toUriString();
}
}- So, finally the SDK has 3 main components:
com.vmware.hercules.foobar.client.api.FooBarServiceApi: These are the client APIs in the SDK that can be used to call the REST endpoint programatically.com.vmware.hercules.foobar.model- Internal classes that were present in
swagger-sdk/**/src - External classes generated from API defs yaml files in
server/**/resources/public
- Internal classes that were present in
Marshalling/Unmarshalling Java Objects
- The SDKs published by the service help the clients, using
RestTemplate, to perform REST operations. These REST operations return json strings. - These strings are actually objects in json string form, that need to be deserialized into java objects.
- RestTemplate has a mechanism of doing this.
RestTemplate::getForObject(url, class)can be used to perform a get operation and serialize the output to a class. - The server and the client need to share this class. They do this by either:
- Copying the implementation of this class from server to the client (duplicate but independent code).
- server publishes the SDK using
swagger-sdkwith these classes present inmodel
ObjectMapper
Jackson ObjectMapperis used to serialize Java objects into JSON and deserialize JSON string into Java objects.
public class Car {
private String color;
private String type;
// standard getters setters
}- Java object to json
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
Car car = new Car("yellow", "renault");
objectMapper.writeValue(new File("target/car.json"), car);
String carAsString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(car);- Json to java object
String json = "{ \"color\" : \"Black\", \"type\" : \"BMW\" }";
Car car = objectMapper.readValue(json, Car.class); - Creating a Java List From a JSON Array String
String jsonCarArray =
"[{ \"color\" : \"Black\", \"type\" : \"BMW\" }, { \"color\" : \"Red\", \"type\" : \"FIAT\" }]";
List<Car> listCar = objectMapper.readValue(jsonCarArray, new TypeReference<List<Car>>(){});Spring configuration
- Spring applications can be configured using
application.propertiesorapplication.yamlfiles. - This file is added to the jar file when the application is built.
- The values in the properties file can be overriden using an external
application.propertiesfile in the same directory as the jar file (or using--key=valuecommand line args when the jar is executed)
java --jar application.jar --serverport=8181- Similar to dependency injection, values can be injected into the application from these properties file, or even from the system environment, using
@Valueannotation.
@Value("string value") // default value
private String stringValue;
@Value("${value.from.file}") // value from a property file
private String valueFromFile;
@Value("${unknown.param:some default}")
private String someDefault;
@Value("${systemValue}") // value from environment
private String systemValue;
@Value("${listOfValues}") // listofValues=foo,bar,baz,bin
private String[] valuesArray;- A group of configurations can also be grouped together in code using a class with
@ConfigurationPropertiesannotation. Add@Configurationannotation to make it a bean, and@Autowiredthis property in other classes.
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("db") // All configs of `db.*` type are parsed to populate this class values.
public class DbSettings {
private String connection;
private String token;
// getters and setters are needed.
}
public class Client {
@Autowired
private DbSettings dbconn;
}- Spring supports multiple profiles. Any profile will use the
application-<profilename>.yamlfile. By default, default profile is active and usesapplication.yamlfile. - A particular profile can be set using
spring.profiles.active: <profilename>configuration in theapplication.yamlfile. - The new profile overrides any configs that is defined in both the default and new profile. For configs that are not overriden, default profile values are taken.
- Profile can be overriden using command line parameters as well:
java -jar my-web-app.jar --spring.profiles.active=prod- Profile can also be used to instantiate specific beans:
@Profile("prod")
@Repository
public class ProductionDatabase {
//...
}- Some microservices can also use external configuration services like
Apache Zookeeper,etcd,Hashicorp Consul,Spring cloud configuration serveretc. Spring cloud config servercan access a git or svc repo, or a hashicorp vault to track configuration values. This way configuration can be version controlled, pushed to prod without requiring the microservices to be rebuilt.- Client microservices use
spring cloud config clientto access these configurations from the config server.
Written on July 24, 2021